Department of Diabetology

Dr. Benedict Aruldas
M.B.B.S, M.MED PGDHSc
Diabetologist
What is Diabetes
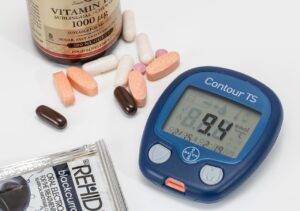 Diabetes is a Chronic health condition that affects how your body converts food into energy.
Diabetes is a Chronic health condition that affects how your body converts food into energy.
Most of the food you eat is broken down into Glucose and released into your bloodstream. When your blood sugar goes up, it signals the Pancreas to release Insulin. Insulin acts like a key to let the blood sugar into your body’s cells for use as energy.
If you have Diabetes, your body either doesn’t make the required Insulin or cannot use the Insulin it makes as it should. When there isn’t enough Insulin then too much blood sugar stays in your bloodstream.
Over time, high Glucose in the blood can cause serious health problems, such as heart disease, vision loss, and kidney disease. There isn’t a cure yet for Diabetes, but losing excess weight, healthy food habbits and being active through the day can reducethe impact of Diabetes in our life. Taking medicine as needed, self-management and keeping good health can also reduce the impact of Diabetes.
Screening For Diabetes
- Brain (stroke) Nerve Damage (neuropathy)
- Heart (heart attack)
- Leg (gangrene)
- High blood pressure
- Kidney Damage (kidney failure)
- High infection rates.
- Eye Damage (retinopathy)
Screening for Diabetes complications hence should be thoroughly and extensively.
Eye Screening: Diabetics are 25 times more prone to eye diseases known as Retinopathy. Hence special attention is given to the eye by a team of doctors.
Heart Check Up: Tests done for ECG, Treadmill, Echo and Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy Screening. Diabetic Patients do not experience any chest pain at the time of an heart attack, hence it is vital for the patients to undergo a complete Heart Checkup atleast once in a Year.
Kindney Function Test : Annual screening for Micro Albuminuria Renal Function Tests and Renal Ultrasonography. Kidney disease due to Diabetes, if detected at an early stage is completely reversible. Hence it is important to undergo a Kidney Function Test once in a year especially for patients who are above 50 years of age.
Neuropathy Screening: Numbness in the foot and hand, tingling sensations, burning pain in the legs and foot, are the symptoms of Diabetic Neuropathy. Tests through Biothesiometry, HCP Study are used to check if the Patient is affected by Neuropathy.
Foot Study: Improper foot care may lead to foot ulcers which may turn gangrenous. This in turn leads to amputation of legs.
Tests and Treatments for Diabetes
Tests for Diabetes starts from a one time visit to assess the state of diabetes and complications. And continue with treatment of Diabetes
Patients who develop type-I diabetes are considered to be in emergency where treatment needs to be delivered to these patients immediately,
More about Types of Diabetes
There are three main types of Diabetes: Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational Diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes is thought to be caused by an autoimmune reaction where the body attacks itself by mistake that stops your body from making Insulin. Approximately 5-10% of the people who have Diabetes have type 1. Symptoms of type 1 Diabetes often develop quickly. It’s usually diagnosed in children, teenagers, and young adults. If you have type 1 Diabetes, you’ll need to take Insulin every day to survive. Currently, no one knows how to prevent type 1 Diabetes.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes : With type 2 Diabetes, your body doesn’t use Insulin well and can’t keep blood sugar at normal levels. About 90-95% of people with Diabetes have type 2. It develops over many years and is usually diagnosed in adults but more and more in children, teenagers, and young adults. You may not notice any symptoms, so it’s important to get your blood sugar tested if you’re at risk. Type 2 Diabetes can be prevented or delayed with healthy lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, eating healthy food, and being active.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational Diabetes develops in pregnant women who have never had Diabetes. If you have gestational Diabetes, your baby could be at higher risk for health problems. Gestational Diabetes usually goes away after your baby is born but increases your risk for type 2 Diabetes later in life.
